
If you’re living abroad but dreaming of starting a company in the UAE, you’re not alone. The country has become one of the top choices for global founders who want quick setup, investor-friendly rules, and access to Middle Eastern and international markets. But many first-time entrepreneurs feel overwhelmed—especially when they are not physically in the UAE. That’s where this Business Setup UAE for Non-Residents guide comes in.
Here, you’ll find a step-by-step roadmap that explains how to start business Dubai remote, what UAE authorities expect, how foreign investor UAE pathways work, and what to do after you open company Dubai successfully.
Thinking beyond setup? Want a property for your business? Here’s how to get mortgage-ready in UAE once your company is live.
Why UAE Attracts Non-Resident Entrepreneurs
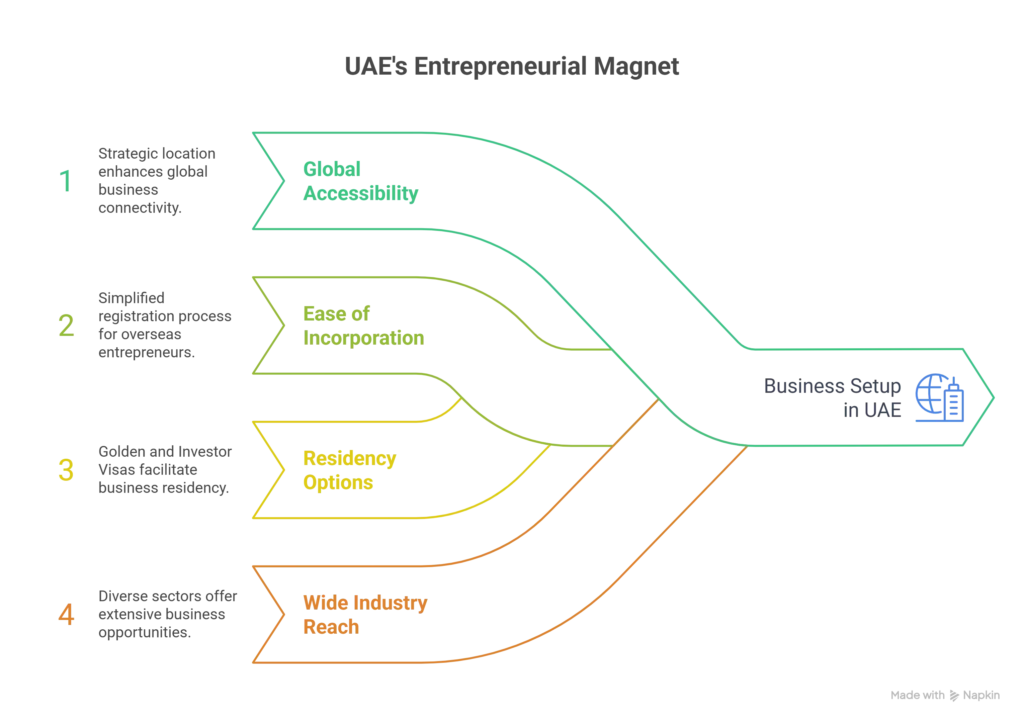
The UAE is more than just a tax-friendly destination. For overseas business owners, it offers:
- Global accessibility: Strategic location between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- Ease of incorporation: Simplified steps to register without needing to stay in UAE.
- Residency options: Golden Visa and Investor Visa pathways for business owners.
- Wide industry reach: From real estate and oil & gas to digital marketing and solar energy.
This makes business setup UAE for non-residents a clear pathway to enter and grow in the Middle East market.
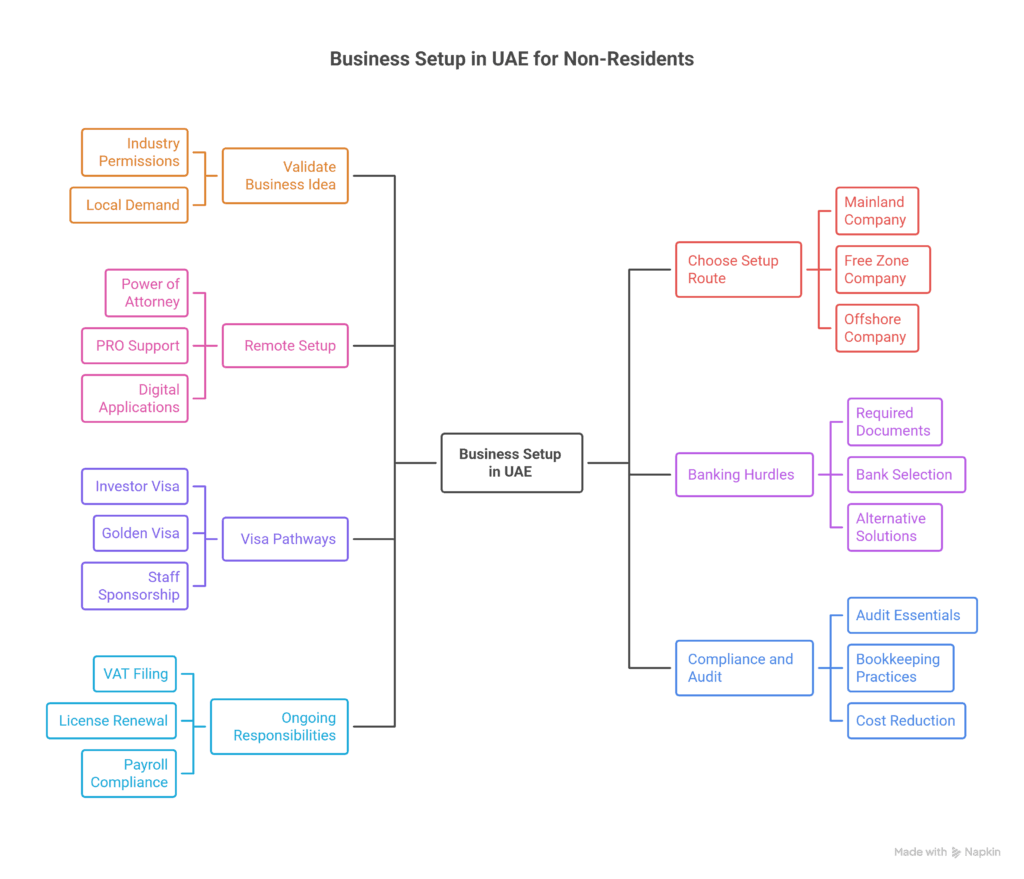
Step 1: Validate Your Business Idea
Before investing, make sure your business idea aligns with UAE regulations and market demand.
Industry Permissions for Foreign Investor UAE
Not all industries are open for 100% foreign ownership. Some sectors, like trading, services, and technology, are open, while mining or oil often require local partnerships.
Aligning with Local Demand
Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and other Emirates have unique strengths—digital services thrive in Dubai, while Abu Dhabi leads in energy and real estate.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Setup Route
When you open company Dubai as a non-resident, the biggest decision is choosing between mainland, free zone, or offshore setups.
Mainland Company Formation
- Allows you to trade directly in the UAE market.
- Needed if you plan to work with government contracts.
- Some activities may require Emirati partnership.
Free Zone Company Formation
- 100% ownership for non-residents.
- Easy license renewals.
- Restrictions on direct trade within mainland.
Offshore Companies
- Popular for holding and investment purposes.
- No physical office needed.
- Not suitable for local trading.
Step 3: Remote Setup for Non-Residents
One of the biggest concerns is how to start business Dubai remote. The UAE makes it possible through:
Power of Attorney (POA)
Allows an authorized agent to complete setup steps on your behalf.
PRO and Agent Support
Professional agents handle documentation, attestation, and government approvals.
Digital Applications
Many free zones now allow digital submission of documents and e-signatures.
Setting up from overseas? Our team offers end-to-end remote support for your UAE business launch.
Step 4: Handling Banking Hurdles
For a foreign investor UAE, opening a bank account is often more complex than company registration.
Documents Needed
- Trade license
- Passport copies
- Proof of address abroad
- Business plan and invoices
Choosing the Right Bank
Some banks require high minimum balances. International banks may be easier for non-residents than local banks.
Alternative Solutions
If bank account approval takes time, payment providers and fintech solutions can bridge the gap.
Want a smoother process? Get mortgage-ready with a corporate account that supports your property purchase and future investments.
Step 5: Visa Pathways for Non-Resident Founders
To make your business setup UAE for non-residents sustainable, visas are essential.
Investor Visa
Grants residency rights to company owners. Renewable every 2–3 years.
Golden Visa
Long-term residency for significant investors or entrepreneurs. Offers 5–10 years validity.
Staff Sponsorship
Once you open company Dubai, you can sponsor employees, family members, and dependents.
Step 6: Compliance and Audit Preparation
After registration, staying compliant ensures your company runs without penalties.
UAE Compliance Audit Essentials
Annual audits are mandatory for most companies. Auditors review VAT, payroll accuracy, and financial statements.
Bookkeeping Best Practices
Keep digital and physical copies of invoices, contracts, and receipts.
Reducing Audit Costs
Proper bookkeeping reduces errors, saves auditor time, and lowers fees.
Step 7: Ongoing Responsibilities
Business setup doesn’t end at incorporation. Ongoing requirements include:
- VAT filing (quarterly or monthly).
- Renewing trade license annually.
- Payroll WPS compliance to pay employees legally.
- Corporate governance for shareholder and board meetings.
These keep your open company Dubai status active and legally recognized.
Fresh Additions Missing in Other Guides
Unlike generic blogs, here’s what non-residents truly need:
Staff Preparation for Audits
Auditors may interview staff. Train your team on basic company policies and payroll compliance.
Mortgage and Real Estate Options for Business Owners
As a foreign investor UAE, your company can apply for commercial mortgages once you have audited accounts and stable revenues.
How to Cut Costs While Abroad
Remote founders often overspend on PRO and agent services. Bundled consultancy support reduces costs.
FAQ
Can I complete a business setup UAE for non-residents fully online?
Yes, in many free zones you can register remotely with digital signatures, though some activities still require notarized documents.
Is it possible to start business Dubai remote without visiting once?
Yes, through POA and agent services. However, bank account opening may need your physical presence depending on the bank.
What type of visa do I get as a foreign investor UAE?
You can apply for an Investor Visa or Golden Visa, depending on your capital, business type, and eligibility.
Do I need a local sponsor to open company Dubai?
Not always. Free zones allow 100% ownership, while some mainland activities may still require local involvement.
What are the common mistakes non-residents make?
Delays in banking, ignoring VAT registration, and poor record-keeping are frequent issues that can be avoided with expert guidance.







1 Comment
[…] Which Free Zone is right? From confusion to clarity — let’s make your UAE business setup simple. […]